The vine copula (Vinecop) API
Import the libraries
[22]:
import pyvinecopulib as pv
import numpy as np
A first vine copula
[23]:
# Specify pair-copulas
bicop = pv.Bicop(pv.bb1, 90, parameters=np.array([[1.0], [2.0]]))
pcs = [[bicop, bicop], [bicop]]
# Specify R-vine matrix
mat = np.array([[1, 1, 1], [2, 2, 0], [3, 0, 0]])
# Set-up a vine copula
cop = pv.Vinecop.from_structure(matrix=mat, pair_copulas=pcs)
print(cop)
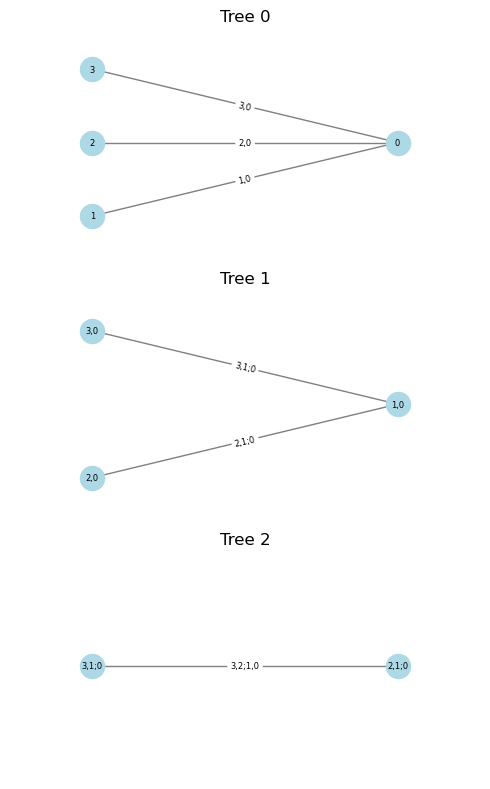
cop.plot()
<pyvinecopulib.Vinecop> Vinecop model with 3 variables
tree edge conditioned variables conditioning variables var_types family rotation parameters df tau
1 1 3, 1 c, c BB1 90 1.00, 2.00 2.0 -0.67
1 2 2, 1 c, c BB1 90 1.00, 2.00 2.0 -0.67
2 1 3, 2 1 c, c BB1 90 1.00, 2.00 2.0 -0.67
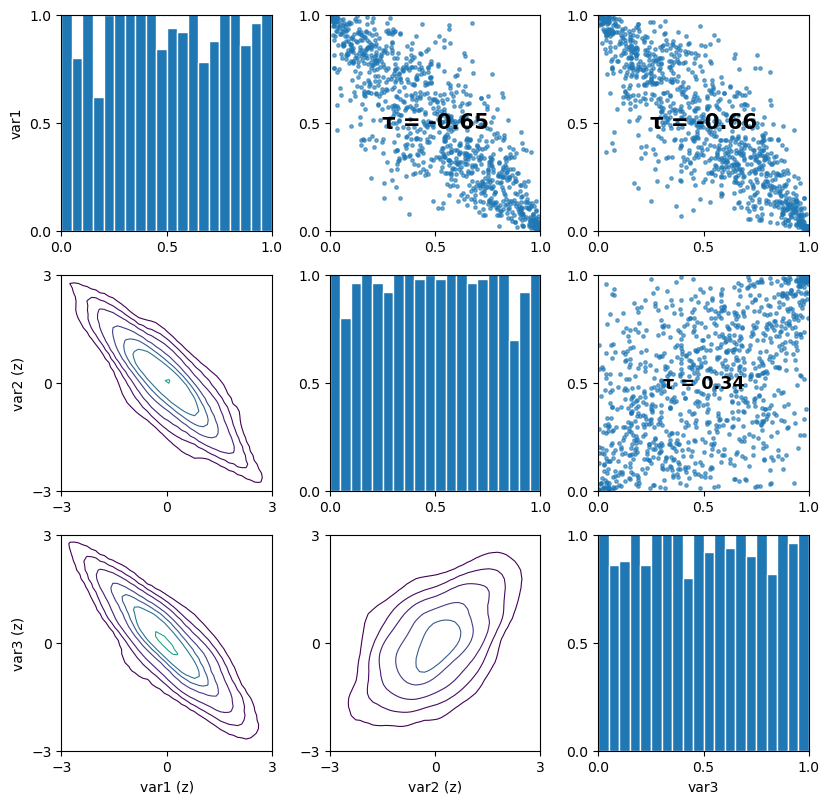
Showcase some methods
[24]:
u = cop.simulate(n=1000, seeds=[1, 2, 3])
pv.pairs_copula_data(u) # Visualize the simulated pair-copula data
[24]:
(<Figure size 840x840 with 9 Axes>,
array([[<Axes: ylabel='var1'>, <Axes: >, <Axes: >],
[<Axes: ylabel='var2 (z)'>, <Axes: >, <Axes: >],
[<Axes: xlabel='var1 (z)', ylabel='var3 (z)'>,
<Axes: xlabel='var2 (z)'>, <Axes: xlabel='var3'>]], dtype=object))
[25]:
# Evaluate various functions for the first 10 samples
u = u[:10, :]
fcts = [
cop.pdf,
cop.rosenblatt,
cop.inverse_rosenblatt,
cop.loglik,
cop.aic,
cop.bic,
]
[f(u) for f in fcts]
[25]:
[array([ 9.64091108, 0.87359882, 14.66737329, 4.67958213,
7.73013565, 8.2626296 , 429.08734894, 10.27557579,
9.6695691 , 31.73104835]),
array([[0.39834572, 0.58306208, 0.62781835],
[0.1638618 , 0.12511687, 0.03259297],
[0.14649436, 0.53506962, 0.19416263],
[0.90118677, 0.97149881, 0.62800446],
[0.61664802, 0.33426639, 0.30274465],
[0.62193432, 0.49491002, 0.29487009],
[0.98701895, 0.15973708, 0.40652872],
[0.6902412 , 0.51336107, 0.37487839],
[0.20454371, 0.13136605, 0.38700309],
[0.13685699, 0.60725771, 0.47552933]]),
array([[0.39834572, 0.633344 , 0.5478186 ],
[0.1638618 , 0.83947886, 0.82385407],
[0.14649436, 0.90468165, 0.77073467],
[0.90118677, 0.14008307, 0.05778318],
[0.61664802, 0.31041658, 0.45172058],
[0.62193432, 0.33993435, 0.39711063],
[0.98701895, 0.00167812, 0.17774749],
[0.6902412 , 0.26458969, 0.35008842],
[0.20454371, 0.78575115, 0.80773584],
[0.13685699, 0.91743568, 0.78274433]]),
24.634294929018786,
-37.26858985803757,
-35.4530793000733]
Different ways to fit a copula (when the families and structure are known)…
[26]:
u = cop.simulate(n=1000, seeds=[1, 2, 3])
# Define first an object to control the fits:
# - pv.FitControlsVinecop objects store the controls
# - here, we only restrict the parametric family
# - see help(pv.FitControlsVinecop) for more details
controls = pv.FitControlsVinecop(family_set=[pv.bb1])
print(controls)
# Create a new object an select family and parameters by fitting to data
cop2 = pv.Vinecop.from_structure(matrix=mat, pair_copulas=pcs)
cop2.select(data=u, controls=controls)
print(cop2)
# Otherwise, create directly from data
cop2 = pv.Vinecop.from_data(data=u, matrix=mat, controls=controls)
print(cop2)
<pyvinecopulib.FitControlsVinecop>
Family set: BB1
Parametric method: mle
Nonparametric method: constant
Nonparametric multiplier: 1
Nonparametric grid size: 30
Weights: no
Selection criterion: bic
Preselect families: yes
mBIC prior probability: 0.9
Truncation level: none (default)
Tree criterion: tau
Threshold: 0
Select truncation level: no
Select threshold: no
Select families: yes
Show trace: no
Number of threads: 1
MST algorithm: mst_prim
<pyvinecopulib.Vinecop> Vinecop model with 3 variables
tree edge conditioned variables conditioning variables var_types family rotation parameters df tau
1 1 3, 1 c, c BB1 270 0.36, 2.54 2.0 -0.67
1 2 2, 1 c, c BB1 90 0.90, 2.00 2.0 -0.66
2 1 3, 2 1 c, c BB1 90 1.03, 2.03 2.0 -0.68
<pyvinecopulib.Vinecop> Vinecop model with 3 variables
tree edge conditioned variables conditioning variables var_types family rotation parameters df tau
1 1 3, 1 c, c BB1 270 0.36, 2.54 2.0 -0.67
1 2 2, 1 c, c BB1 90 0.90, 2.00 2.0 -0.66
2 1 3, 2 1 c, c BB1 90 1.03, 2.03 2.0 -0.68
When nothing is known, there are also two ways to fit a copula…
[27]:
# Create a new object and select strucutre, family, and parameters
cop3 = pv.Vinecop(d=3)
cop3.select(data=u)
print(cop3)
# Otherwise, create directly from data
cop3 = pv.Vinecop.from_data(data=u)
print(cop3)
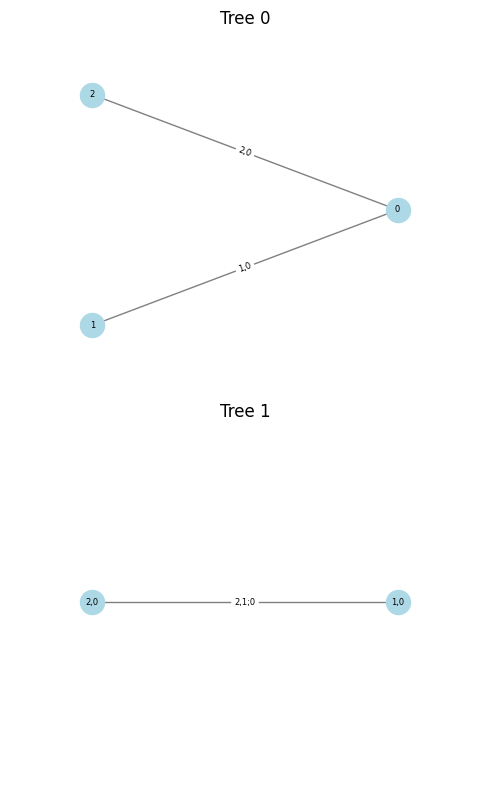
cop3.plot()
<pyvinecopulib.Vinecop> Vinecop model with 3 variables
tree edge conditioned variables conditioning variables var_types family rotation parameters df tau
1 1 2, 1 c, c BB1 90 0.90, 2.00 2.0 -0.66
1 2 1, 3 c, c BB1 90 0.36, 2.54 2.0 -0.67
2 1 2, 3 1 c, c BB1 270 1.03, 2.03 2.0 -0.68
<pyvinecopulib.Vinecop> Vinecop model with 3 variables
tree edge conditioned variables conditioning variables var_types family rotation parameters df tau
1 1 2, 1 c, c BB1 90 0.90, 2.00 2.0 -0.66
1 2 1, 3 c, c BB1 90 0.36, 2.54 2.0 -0.67
2 1 2, 3 1 c, c BB1 270 1.03, 2.03 2.0 -0.68
C-vine structures
[28]:
# create a C-vine structure with root node 1 in first tree, 2 in second, ...
cvine = pv.CVineStructure([4, 3, 2, 1])
# specify pair-copulas in every tree
tree1 = [
pv.Bicop(pv.gaussian, 0, np.array([[0.5]])),
pv.Bicop(pv.clayton, 0, np.array([[3.0]])),
pv.Bicop(pv.student, 0, np.array([[0.4], [4]])),
]
tree2 = [
pv.Bicop(pv.indep),
pv.Bicop(pv.gaussian, 0, np.array([[0.5]])),
]
tree3 = [pv.Bicop(pv.gaussian)]
# instantiate C-vine copula model
cop = pv.Vinecop.from_structure(
structure=cvine, pair_copulas=[tree1, tree2, tree3]
)
print(cop)
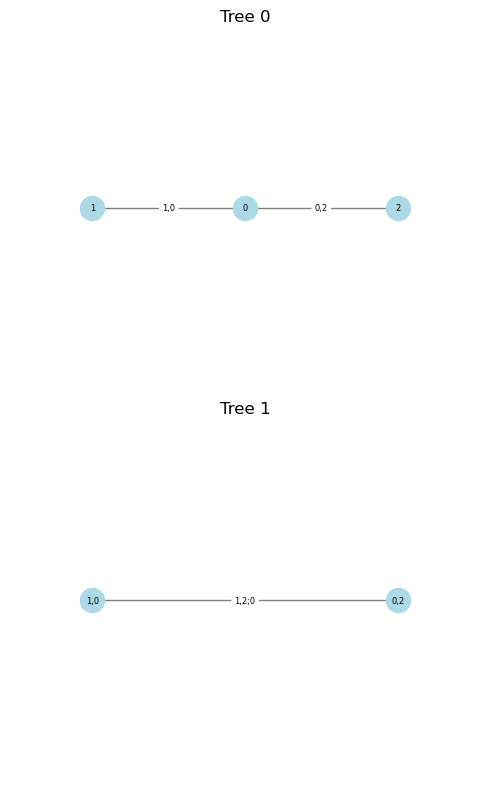
cop.plot()
<pyvinecopulib.Vinecop> Vinecop model with 4 variables
tree edge conditioned variables conditioning variables var_types family rotation parameters df tau
1 1 4, 1 c, c Gaussian 0 0.50 1.0 0.33
1 2 3, 1 c, c Clayton 0 3.00 1.0 0.60
1 3 2, 1 c, c Student 0 0.40, 4.00 2.0 0.26
2 1 4, 2 1 c, c Independence 0.00
2 2 3, 2 1 c, c Gaussian 0 0.50 1.0 0.33
3 1 4, 3 2, 1 c, c Gaussian 0 0.00 1.0 0.00